Climate change is shaping the world our students will inherit, and classrooms play a vital role in preparing them for this reality. Teaching climate literacy is no longer just an add-on to the curriculum, it is becoming a necessity to help young learners understand the planet’s systems, the impact of human activity, and the solutions we can adopt.
For teachers, this shift means adopting new approaches to make climate education engaging, practical, and inspiring. A well-structured teacher training course in Mumbai, for example, equips educators with effective teaching strategies that can be applied across global contexts, showing teachers everywhere how to bring sustainability into everyday learning.
In this blog post, we will explore why climate literacy is becoming central to education and highlight five ways teachers can embed it meaningfully in classrooms.
Why Climate Literacy Matters in Classrooms Today
Climate literacy goes beyond science lessons — it’s about helping students understand how climate issues impact daily life, communities, and future opportunities. When students learn how ecosystems work, how human actions affect the environment, and how solutions can be implemented, they become active citizens who care for the planet.
Global data underscores just how urgent this is:
- The IPCC reports that global temperatures have already risen by 1.1°C since pre-industrial times, and the world could cross 1.5°C within the next decade without immediate action.
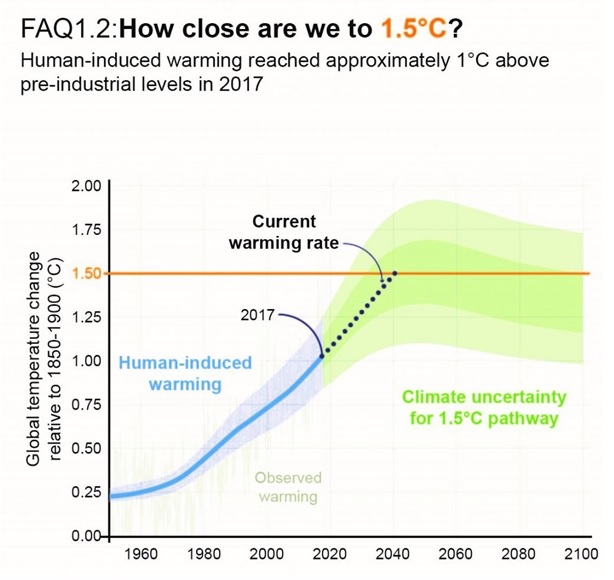
Source: ipcc.ch
- A UNESCO survey (2021) revealed that 70% of young people struggle to grasp climate change and its effects because it isn’t taught systematically in schools.
- According to UNICEF, more than 1 billion children are at “extremely high risk” from climate impacts such as floods, droughts, and air pollution.
For teachers, integrating climate literacy is not only about addressing these alarming realities — it also means preparing students with critical thinking, problem-solving, and empathy, essential skills for the 21st century. By teaching climate literacy, educators give learners the tools to navigate challenges and become part of global solutions.
5 Practical Ways to Integrate Climate Literacy into Teaching
Climate literacy isn’t just about adding new topics to the syllabus, it’s about reshaping how subjects are taught and how students connect lessons to the real world. Below are five practical strategies teachers can use to make classrooms greener and prepare students for a sustainable future.
1. Connecting Lessons to Local and Global Issues
When students see how climate issues affect their own communities, learning becomes personal and impactful. Teachers can link global climate data with local challenges such as air pollution, waste management, or flooding. For instance, discussing deforestation alongside a nearby conservation project helps students understand both the global picture and their role in it.
2. Encouraging Student-Led Sustainability Projects
Hands-on activities allow students to turn knowledge into action. Teachers can guide students to design eco-clubs, recycling drives, or awareness campaigns in their schools. These projects develop leadership, teamwork, and problem-solving skills while instilling a sense of responsibility for the environment.
3. Using Interdisciplinary Approaches
Climate change affects every subject. A math class can calculate carbon footprints, language classes can explore environmental poetry, and art projects can design sustainability posters. By weaving climate themes across disciplines, teachers show students how interconnected the issue is and encourage creativity in finding solutions.
4. Bringing Technology Into Climate Education
Digital tools make climate learning immersive and engaging. Teachers can use interactive simulations to show rising sea levels, virtual field trips to rainforests, or online platforms for global collaboration. Technology helps students visualize problems and solutions, making learning both modern and memorable.
5. Fostering Hope Through Solution-Focused Teaching
Climate change discussions can sometimes feel overwhelming. Teachers can balance this by highlighting success stories, such as renewable energy innovations, community clean-up programs, or student-led campaigns around the world. Focusing on solutions empowers students to see themselves as agents of change rather than passive observers.
Final Thoughts
Climate literacy is no longer optional, it is essential for creating informed, responsible citizens ready to tackle one of the biggest challenges of our time. By integrating sustainability into everyday teaching, educators make classrooms places of awareness, creativity, and action.
For teachers, enrolling in a teacher training course in Mumbai can provide valuable insights into sustainability-focused pedagogy. Such programs highlight effective teaching strategies for educators in Mumbai, which can be adapted globally to make climate literacy practical, engaging, and solution-driven.
When classrooms go green, students not only learn about climate change, they learn how to change the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is climate literacy?
Climate literacy means understanding the science of climate change, its impacts on people and ecosystems, and the actions individuals and communities can take to address it. For students, it helps develop awareness and responsibility toward building a sustainable future.
2. Why is climate literacy important in schools?
Teaching climate literacy equips students with critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. It helps them connect lessons to real-world issues and prepares them to become environmentally responsible citizens.
3. How can teachers integrate climate literacy into regular subjects?
Teachers can link environmental issues to different subjects: calculating carbon footprints in math, analyzing sustainability policies in social studies, exploring eco-literature in language classes, or conducting renewable energy projects in science.
4. What role does technology play in climate education?
Technology brings climate literacy to life through simulations, virtual field trips, and interactive data tools. These digital resources make abstract concepts visible and encourage students to engage actively with the subject.
5. How do teacher training courses support climate literacy?
A well-designed program like, teacher training course in Mumbai, can help educators adopt effective teaching strategies that make climate topics relevant and practical. Training programs prepare teachers to embed sustainability into lessons in ways that inspire student action.
6. Can climate literacy be taught to younger students?
Yes. Climate concepts can be introduced at every grade level. For younger students, it may involve simple activities like recycling or gardening, while older students can explore complex topics such as renewable energy or policy debates.
Written By : Abhishek








